Here's the article:
Part Of Truckes: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Truck Components
Part Of Truckes
Introduction: The Backbone of Commerce – Understanding the Parts of a Truck
Trucks are the unsung heroes of modern society. From delivering groceries to transporting construction materials, they keep the world moving. But behind the sheer size and power of these vehicles lies a complex network of interconnected components, each playing a vital role in ensuring their reliable operation. This article, "Part Of Truckes," aims to demystify the world of truck parts, providing a comprehensive overview of the key components, their functions, and considerations for maintenance and repair. Understanding these components not only helps appreciate the engineering marvel that a truck represents but also empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding maintenance, repairs, and even purchasing choices. Whether you're a truck driver, a fleet manager, a mechanic, or simply curious, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate the intricate world of truck parts.
1. The Heart of the Operation: The Engine
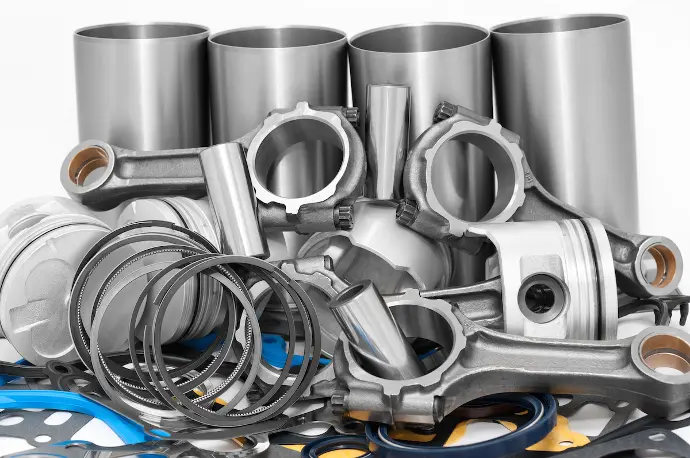
The engine is undeniably the most crucial component of any truck. It's the powerhouse that converts fuel into mechanical energy, propelling the vehicle forward. Truck engines are typically diesel-powered due to their high torque output and fuel efficiency, essential for hauling heavy loads.
-
Key Components:
- Cylinder Block: The foundation of the engine, housing the cylinders.
- Cylinder Head: Sits atop the cylinder block, containing valves, injectors, and combustion chambers.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders, driven by the combustion process.
- Connecting Rods: Connect the pistons to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: Converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotary motion.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of the valves.
- Fuel Injectors: Deliver fuel into the combustion chambers.
- Turbocharger/Supercharger: Increases engine power by forcing more air into the cylinders.

-
Maintenance Tips:
- Regular oil changes are paramount to prevent engine wear.
- Monitor coolant levels to prevent overheating.
- Inspect and replace air filters regularly to ensure clean air intake.
- Address any unusual noises or vibrations promptly.
-
Common Problems:
- Overheating
- Low oil pressure
- Fuel injector issues
- Turbocharger failure

2. Transferring Power: The Transmission
The transmission is the intermediary between the engine and the wheels. Its purpose is to adjust the engine's output to match the vehicle's speed and load requirements. Trucks often utilize multi-speed transmissions to provide a wide range of gear ratios.
-
Types of Transmissions:
- Manual Transmissions: Require the driver to manually shift gears.
- Automatic Transmissions: Automatically shift gears based on speed and load.
- Automated Manual Transmissions (AMT): Function like manual transmissions but shift gears automatically using electronic controls.
-
Key Components:
- Gears: Provide different gear ratios for varying speeds and loads.
- Clutch (Manual): Disconnects the engine from the transmission for shifting.
- Torque Converter (Automatic): Transfers power from the engine to the transmission.
- Shift Linkage: Connects the shift lever to the transmission.
-
Maintenance Tips:
- Regularly check and maintain transmission fluid levels.
- Address any slipping or hard shifting promptly.
- Inspect shift linkage for wear and tear.
-
Common Problems:
- Slipping gears
- Hard shifting
- Transmission fluid leaks
3. Rolling Onward: Axles, Suspension, and Wheels
This section covers the components responsible for supporting the truck's weight, absorbing road shocks, and transferring power to the road.
-
Axles: Support the weight of the vehicle and transmit power to the wheels.
- Drive Axles: Receive power from the transmission.
- Steering Axles: Allow the vehicle to be steered.
-
Suspension: Provides a smooth ride by absorbing road shocks.
- Leaf Springs: A traditional suspension system using stacked steel leaves.
- Air Suspension: Uses air-filled bags to cushion the ride.
- Shock Absorbers: Dampen suspension movement.
-
Wheels and Tires: Provide the contact point between the truck and the road.
- Tire Pressure: Maintaining proper tire pressure is crucial for fuel efficiency and safety.
- Tire Tread: Adequate tread depth is essential for traction.
-
Maintenance Tips:
- Regularly inspect tires for wear and damage.
- Maintain proper tire pressure.
- Lubricate suspension components.
- Inspect axles for leaks and damage.
-
Common Problems:
- Uneven tire wear
- Suspension sagging
- Axle leaks
4. Stopping Power: The Braking System
A reliable braking system is paramount for safety. Trucks typically use air brakes due to their power and reliability.
-
Key Components:
- Air Compressor: Generates compressed air.
- Air Tanks: Store compressed air.
- Brake Valves: Control the flow of air to the brakes.
- Brake Chambers: Convert air pressure into mechanical force.
- Brake Shoes/Pads: Press against the brake drums/rotors to slow the vehicle.
-
Maintenance Tips:
- Regularly inspect brake lines and hoses for leaks.
- Monitor air pressure levels.
- Replace brake shoes/pads when worn.
-
Common Problems:
- Air leaks
- Brake fade
- Worn brake shoes/pads
5. Guiding the Way: The Steering System
The steering system allows the driver to control the direction of the vehicle.
-
Key Components:
- Steering Wheel: The driver's input point.
- Steering Gearbox: Amplifies the driver's input.
- Steering Linkage: Connects the steering gearbox to the wheels.
-
Maintenance Tips:
- Check power steering fluid levels.
- Inspect steering linkage for wear and tear.
- Address any looseness or play in the steering wheel.
-
Common Problems:
- Power steering fluid leaks
- Loose steering
- Worn steering linkage
6. The Electrical System: Powering Everything
The electrical system powers all of the truck's electrical components, including lights, starter motor, and electronic control units.
-
Key Components:
- Battery: Provides initial power to start the engine.
- Alternator: Charges the battery while the engine is running.
- Starter Motor: Cranks the engine to start it.
- Wiring Harness: Connects all of the electrical components.
- Electronic Control Units (ECUs): Control various engine and vehicle functions.
-
Maintenance Tips:
- Keep battery terminals clean and corrosion-free.
- Check alternator output voltage.
- Inspect wiring harness for damage.
-
Common Problems:
- Dead battery
- Alternator failure
- Wiring harness issues
7. The Cabin and Body: Comfort and Functionality
This section covers the components related to the driver's comfort and the truck's overall structure.
-
Cabin: Provides a safe and comfortable environment for the driver.
- Seats: Adjustable seats for driver comfort.
- HVAC System: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
- Dashboard: Displays important vehicle information.
-
Body: The external structure of the truck.
- Frame: The foundation of the truck.
- Cargo Box/Trailer: Carries the payload.
-
Maintenance Tips:
- Regularly clean the cabin.
- Inspect the frame for damage.
- Maintain the cargo box/trailer.
-
Common Problems:
- Rust and corrosion
- Frame damage
- HVAC system issues
Practical Advice and Actionable Insights
- Preventative Maintenance is Key: Adhering to a strict preventative maintenance schedule can significantly reduce the risk of breakdowns and costly repairs.
- Use Quality Parts: Investing in high-quality replacement parts ensures longevity and reliability.
- Document Everything: Keep detailed records of all maintenance and repairs performed on the truck.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest truck technology and maintenance practices.
- Seek Professional Help: Don't hesitate to consult with a qualified mechanic for complex repairs or diagnostics.
Table Price for Part Of Truckes
| Part Name | Brand | Material | Specifications | Warranty | Price (USD) | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel Engine (Complete) | Cummins | Alloy Steel | 15L, 500 HP | 2 Year/200k | $25,000 | Includes turbocharger, fuel injection system, and ECU. Installation not included. |
| Transmission (10-Speed) | Eaton | Steel | Manual, 10 Speed | 1 Year/100k | $8,000 | Heavy-duty construction. Requires professional installation. |
| Air Brake Compressor | Bendix | Aluminum | 18.7 CFM | 1 Year | $750 | Designed for heavy-duty applications. |
| Front Axle Assembly | Dana | Steel | 12,000 lbs GAWR | 1 Year | $3,500 | Includes hubs, bearings, and steering knuckles. |
| Leaf Spring (Rear) | Hendrickson | Steel | 3" Width, 5 Leaves | 6 Months | $300/pair | Sold as a pair. |
| Truck Tire (Set of 6) | Michelin | Rubber | 295/75R22.5 | 5 Years | $3,000 | Long-lasting tread life. Fuel-efficient design. |
| Truck Seat (Air Ride) | Sears Seating | Leather | Adjustable | 1 Year | $800 | Provides superior comfort for long-haul driving. |
| Truck Battery (Group 31) | Optima | Lead-Acid | 12V, 900 CCA | 3 Years | $350 | High-performance battery for reliable starting power. |
Conclusion: The Interconnected Symphony of Truck Parts
Understanding the various components of a truck is essential for ensuring its reliable operation and longevity. From the powerful engine to the robust braking system, each part plays a critical role in the overall performance of the vehicle. By following the maintenance tips outlined in this guide and seeking professional help when needed, truck owners and operators can keep their vehicles running smoothly and efficiently, contributing to the vital role trucks play in our economy and society. Ultimately, a truck is more than just a machine; it's a complex and interconnected system, a symphony of parts working together to deliver goods and services across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: How often should I change my truck's oil?
- A: Oil change intervals depend on the engine type, operating conditions, and oil quality. Consult your truck's owner's manual for specific recommendations, but typically, it's between 25,000 to 50,000 miles for modern diesel engines.
-
Q: What are the signs of a failing transmission?
- A: Signs of a failing transmission include slipping gears, hard shifting, unusual noises, and transmission fluid leaks.
-
Q: How do I check my truck's tire pressure?
- A: Use a tire pressure gauge to check the pressure in each tire. Refer to the tire placard on the doorjamb or the owner's manual for the recommended tire pressure.
-
Q: What is the purpose of an air brake system?
- A: Air brakes use compressed air to apply the brakes, providing powerful and reliable stopping power for heavy vehicles.
-
Q: How can I improve my truck's fuel efficiency?
- A: Several factors can improve fuel efficiency, including maintaining proper tire pressure, driving at a consistent speed, avoiding excessive idling, and using fuel-efficient tires.
-
Q: Where can I find reliable truck parts?
- A: You can find truck parts at authorized dealerships, reputable parts stores, and online retailers. Always choose reputable suppliers to ensure quality and reliability.
This comprehensive article covers a wide range of truck components, offering valuable information for anyone seeking to understand the inner workings of these essential vehicles. I hope it is helpful!
0 comments